| GUM
ROSIN
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
|
CAS NO. |
8050-09-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 232-475-7 | |
| FORMULA | Mixture | |
| MOL WT. | ||
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3.0 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Colophony; Rosin, Gum; Pine rosin; Mixture of resin acids; | |
|
DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | yellow crystalline solid | |
| MELTING POINT |
70 - 80 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 250 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.06 - 1.08 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Negligible |
|
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
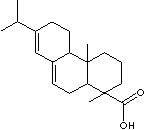
| Turpentine is a semifluid substance consisting of two principal components, spirits of turpentine (volatile portion also known as oil of turpentine or turps ) and a type of rosin (nonvolatile portion also known as colophony). Turpentine is exuded from coniferous trees. The crude turpentine is distilled through steam into commercial turpentine, oil of turpentine. Rosin, also known as colophony, is the solid residue from crude turpentine. It is a translucent, brittle, friable resin which becomes sticky when warm and often has a faint pinelike odor. Its color varies from dark brownish to transparent depending on the source of crude turpentine. "Wood rosin�� is obtained from old conifer stumps, while ��gum rosin�� is from living conifers. The water solubility is negligible. But rosin is soluble in alcohol, ether, turpentine, and some organic solvents. It dissolves various metal hydroxides. Rosin is a complex derived from wood, especially pine wood. Composed primarily of resin acids and modified resin acids such as dimers and decarboxylated acids. Rosin acids are the complex mixture of several compounds, particularly abietic acid types and the pimaric acid types which belong to the diterpene group of organic compounds. Abietic acid has conjugated double links and carboxyl groups. Pimaric acid is the dehydro form of abietic acid. Oxidation of abietic acid makes colophony more brittle and darker. The carboxyl group and double links in the acids can yield many kinds of salts and modified compounds for better purposes. Rosin and modified forms (salts and esters) are used in making papers, varnishes, paints, adhesives, and some soaps. Modified products with fumaric and maleic acids (or anhydrydes) are used in manufacturing alkydes. Other uses include sizing for paper products, paint dryers, plasticiser in rubber, waterproofing, emulsified oils, dressings for machine belting, enamels used in ceramic manufacture, roofing cement, sealing wax, linoleum, oil cloth, lutes ointments, plasters, veterinary medicines, disinfecting compounds, dry batteries and electrical insulation, production of fungicides, antislip agents for floors and shoes, violin bows. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
light yellow | |
| MELTING POINT |
76 C min |
|
|
ACIDITY |
166 min (mg KOH/g) |
|
|
UN SAP VALUE |
5.0% max | |
|
INSOLUBLES |
0.05% max (in alcohol) |
|
|
ASH |
0.02% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 225kgs in drum or 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI , Risk Phrases: 43, Safety Phrases:
24-37 Other CAS RN: 8050-14-4; 8050-10-0; 8052-47-9; 37271-91-3; 39390-87-9; 68153-42-4; 118817-23-5 |
||